Mission
To reduce the number of cases and deaths due to breast and cervical cancer, among women with limited access to healthcare.
To make Yap become the first island in the world to reach WHO's elimination target for cervical cancer of less than 4 cases of cervical cancer per 100,000 women per year.
Target
Age 30 to 50 years
All women between the ages of 30 to 50 are recommended to have regular screening.
Test Methods
Currently there are 3 methods in which a screening test can be performed
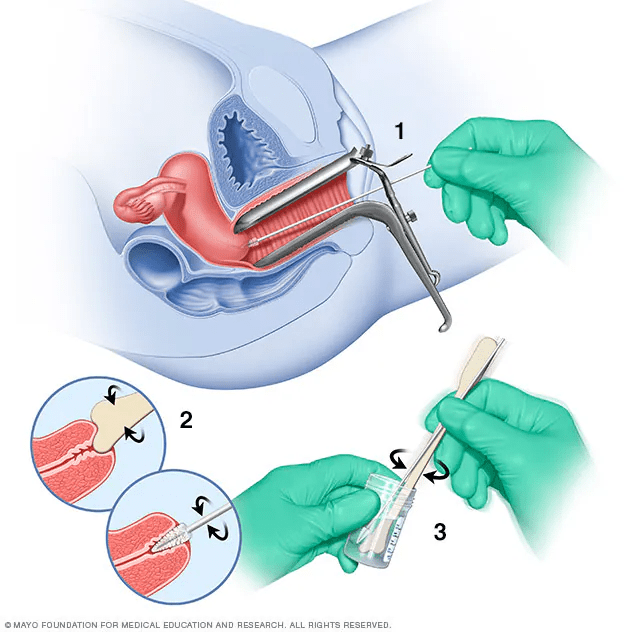
1. Pap Smear
In a Pap test, a vaginal speculum holds the vaginal walls apart to show the cervix. Next, a sample of cells from the cervix is collected using a small cone-shaped brush and a tiny plastic spatula (1 and 2). The brush and spatula are rinsed in a liquid-filled vial (3) and the vial goes to a laboratory for testing.
3. HPV DNA
The test is a screening test for cervical cancer, but the test doesn't tell you whether you have cancer. Instead, the test detects the presence of , the virus that causes cervical cancer, in your system. Certain types of HPV — including types 16 and 18 — increase your cervical cancer risk.